Proteins (or proteins) are essential components of food (along with fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals and water).
According to experts, their share in the daily diet should make up 10 – 15%. Today we’ll talk about the structure as well different types of proteins.
Simple and complex, animal and vegetable, full-fledged and defective proteins – what is their difference.

Proteins are high molecular weight substances with complex structure. We are not able to assimilate them in the form in which they come with food, because for us they are strangers.
Therefore, getting into the body, food proteins break down into small structural units are amino acids. It is from amino acids our body creates its own proteins unique to it, which subsequently uses for their needs.
As you know, our skin, hair, nails, muscles and etc. In addition, proteins (proteins) are an integral part sports nutrition.
There are 20 amino acids in total. They contain oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, sometimes sulfur and phosphorus.
Some amino acids are formed in the body itself due to intestinal bacteria. Such amino acids are called interchangeable.

But there are also 8 indispensable amino acids:
- tryptophan;
- lysine;
- valine;
- leucine;
- isoleucine;
- phenylalanine;
- methionine;
- threonine;
- as well as histidine (for children).
Essential amino acids are absent in the body, therefore must come with food.
It is worth noting that in the human body there are about 5 million different proteins, each of which fulfills its specific function.
Proteins owe their variety to amino acids. The latter, connecting with each other, form the most diverse combinations.
Consider the types of proteins in more detail:
1. Simple and complex. The first ones consist only of amino acids (protein part), the latter also includes prosthetic group (non-protein part).
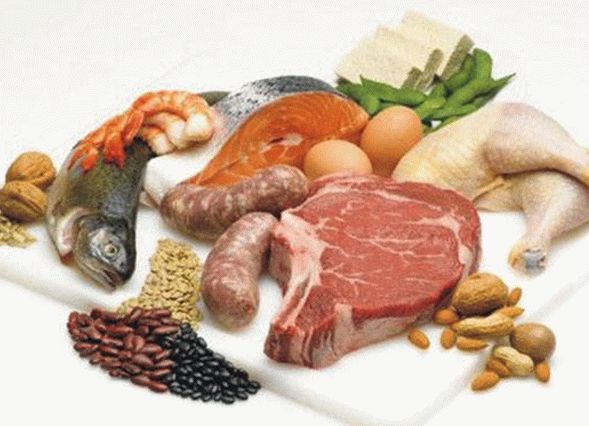
2. Animals (meat, fish, poultry, dairy products) and vegetable (nuts, soybeans, peas, beans). At the same time, animal proteins should account for about 60%
3. Complete and defective proteins. Complete proteins include all essential amino acids that do not form on their own in the body.
Complete proteins are found in animal products. origin, as well as some plant foods (peas, beans, soy).
It’s worth noting that the most valuable is egg white protein, which contains a complete set of amino acids in the right proportions.
In addition, 200 g of beef or 200 g of cod or 1.5 liters of milk able to provide the human body weighing 70 kg with all essential amino acids.

In defective proteins, certain essential amino acids contained in small quantities or completely are absent.
Many plant proteins are inferior, for example, some cereals (wheat, barley and others). They are poor in lysine tryptophan, threonine and methionine.
To increase the biological value of bread, they add to it lysine.
4. Globular (have a spherical shape) and fibrillar (have an elongated filiform form).
Some globular proteins, such as albumin and globulin, found in egg white, milk, and blood serum.
Sources of others, such as glutelins and prolamins, are vegetable proteins (wheat, barley, corn and others).
Fibrillar proteins are mainly animal proteins and perform a structural function in the body.
These include collagen (protein of cartilage, bone and connective tissue), elastin (muscle connective tissue protein, ligaments and blood vessels), keratins (proteins of the skin, hair and nails).
5. High quality (meat, fish, poultry, soybeans, eggs, cheese, milk) and low-quality (potatoes, pasta, rice, bread, nuts, beans).

So, we learned what proteins are made of, how they differ complete proteins from inferior ones, and also met with others types of proteins.
In the next article, we will talk about how protein is useful for organism, what are its functions.